Median Nerve
Injury to the median nerve can lead to many pathological findings. Clinical manifestations differ depending on whether the nerve is injured proximally or distally (i.e., closer to the wrist).
- Distal median nerve injury
- Causes of distal median nerve injury
- Carpal tunnel syndrome
- Can result when carpal tunnel is narrowed due to
- Inflammation of flexor retinaculum
- Inflammation of synovial sheaths of flexor tendons
- Structural changes in carpal bones due to arthritis
- Lunate dislocation
- Wrist laceration (e.g., attempted suicide by wrist slashing)
- Movements lost
- Thumb opposition
- Flexion of proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints in digits 1, 2, and 3
- Flexion of distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints in digits 2 and 3
- Flexion of metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints in digits 2 and 3
- Movement lost because digital branches of median nerve supply first and second lumbricals
- Proximal median nerve injury
- Causes of proximal median nerve injury
- Supracondylar fracture of humerus
- Movements lost
- Pronation
- Thumb opposition
- Flexion of proximal interphalangeal (PIP) joints in digits 1, 2, and 3
- Flexion of distal interphalangeal (DIP) joints in digits 2 and 3
- Flexion of metacarpophalangeal (MCP) joints in digits 2 and 3
- Movement lost because digital branches of median nerve supply first and second lumbricals
- Pathology
- Hand of benediction
- If the patient is asked to make a fist, digits 2 and 3 will remain partially extended. This is because the first and second lumbricals are innervated by the median nerve.
- Ape hand
- Movement is limited to flexion and extension of thumb in plane of palm.
- Flattening of thenar eminence
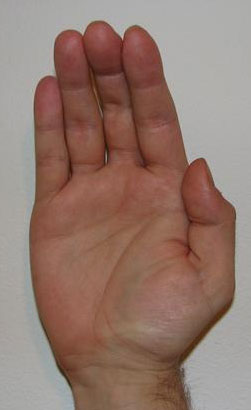
from http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Apehand_1.JPG
- Pronator syndrome
- Occurs when median nerve gets trapped between the heads of the pronator teres muscle
