Learn
Upper: Shoulder, Pectoral Region, and Axilla, Arm, Forearm, HandLower: Gluteal Region, Thigh, Leg, Foot
Learn: Gluteal Region
The gluteal muscles are divided into a superficial layer and a deep layer.
SUPERFICIAL LAYER
This card has been intentionally left blank.
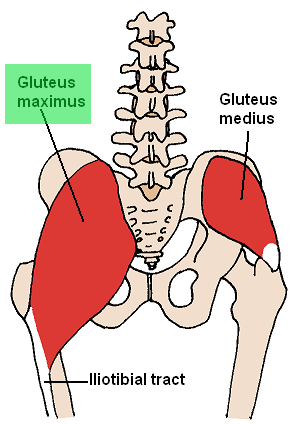
Gluteus maximus muscle
| Origin | Fascia that covers gluteus medius, ilium posterior to posterior gluteal line, fascia of erector spinae, dorsal surface of sacrum, lateral margin of coccyx, sacrotuberous ligament |
| Insertion | Iliotibial tract of fascia lata (which inserts into lateral condyle of tibia) and gluteal tuberosity of proximal femur |
| Innervation | Inferior gluteal nerve |
| Artery | Inferior gluteal artery, superior gluteal artery, first perforating branch of profunda femoris artery |
| Action | Extends femur at hip joint, especially from flexed position; laterally stabilizes hip joint and knee joint; laterally rotates and abducts thigh |
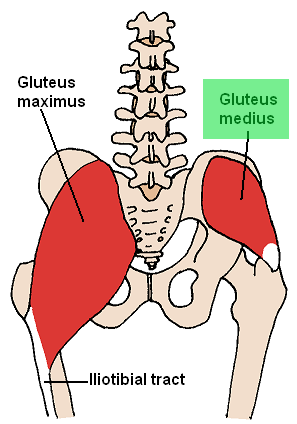
Gluteus medius muscle
| Origin | External surface of ilium, between anterior and posterior gluteal lines |
| Insertion | Lateral surface of greater trochanter of femur |
| Innervation | Superior gluteal nerve |
| Artery | Superior gluteal artery |
| Action | Abducts and medially rotates femur at hip joint; during walking, keeps the pelvis stable over the stance leg, which prevents the pelvis from dropping on the swing side |
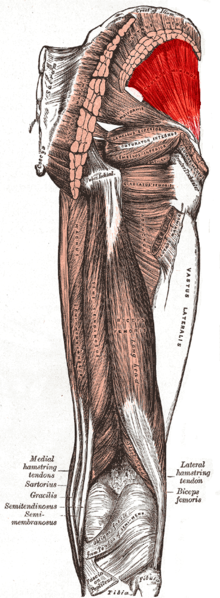
Gluteus minimus muscle
| Origin | External surface of ilium, between anterior and posterior gluteal lines |
| Insertion | Anterior surface of greater trochanter of femur |
| Innervation | Superior gluteal nerve |
| Artery | Superior gluteal artery |
| Action | Abducts and medially rotates femur at hip joint; during walking, keeps the pelvis stable over the stance leg, which prevents the pelvis from dropping on the swing side |
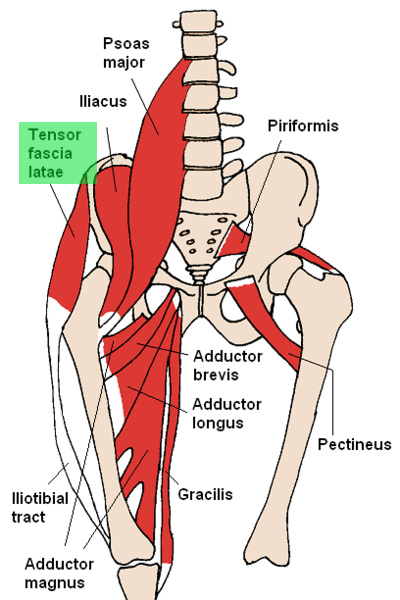
Tensor fascia latae muscle
| Origin | Anterior superior iliac spine; anterior part of iliac crest |
| Insertion | Iliotibial tract |
| Innervation | Superior gluteal nerve |
| Artery | Superior gluteal artery, lateral circumflex femoral artery |
| Action | Abducts and medially rotates the thigh; assists in flexing thigh; stabilizes the knee in extension |
DEEP LAYER
This card has been intentionally left blank.
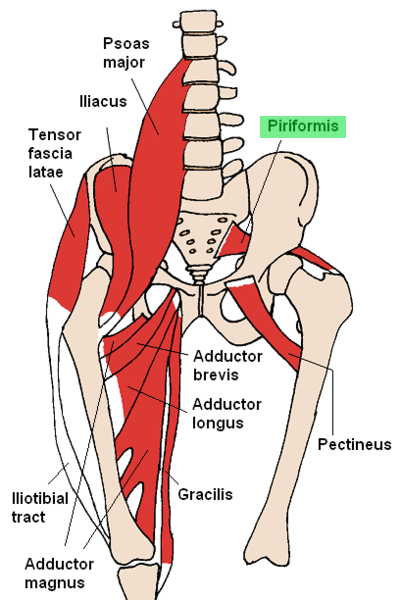
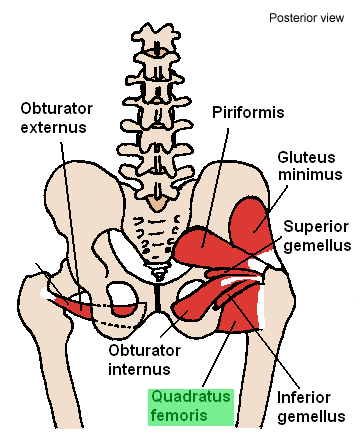
Piriformis muscle
| Origin | Anterior surface of sacrum between anterior sacral foramina |
| Insertion | Medial side of superior border of greater trochanter of femur |
| Innervation | Nerve to piriformis muscle (S1,S2) |
| Artery | Superior gluteal artery; inferior gluteal artery; internal pudendal artery |
| Action | Laterally rotates the extended femur at hip joint; abducts flexed femur at hip joint |
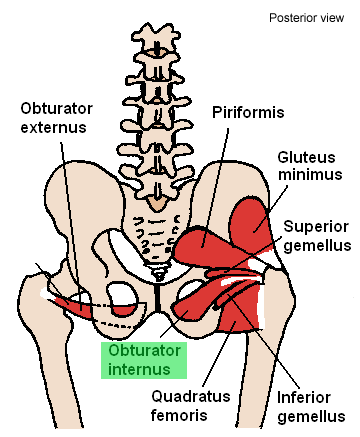
Obturator internus muscle
| Origin | Deep surface of obturator membrane and surrounding bone |
| Insertion | Medial side of greater trochanter of femur |
| Innervation | Nerve to obturator internus |
| Artery | Internal pudendal artery; superior gluteal artery; inferior gluteal artery |
| Action | Laterally rotates the extended femur at hip joint; abducts flexed femur at hip joint |
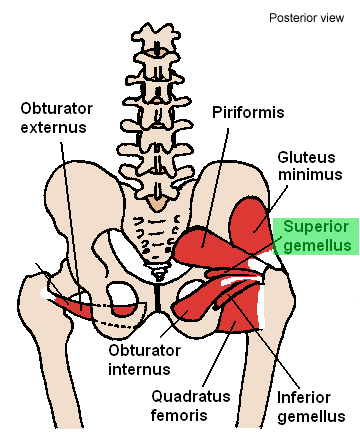
Superior gemellus muscle
| Origin | Ischial spine |
| Insertion | Superior surface of the obturator internus tendon; medial side of greater trochanter of femur with obturator internus tendon |
| Innervation | Nerve to obturator internus |
| Artery | Inferior gluteal artery |
| Action | Laterally rotates the extended femur at hip joint; abducts flexed femur at hip joint |
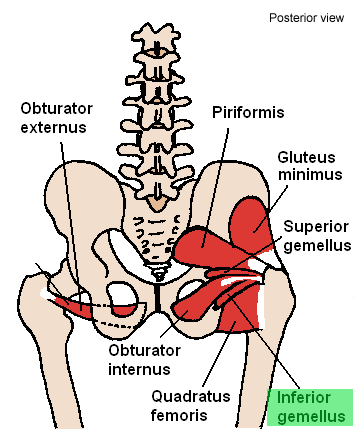
Inferior gemellus muscle
| Origin | Ischial tuberosity |
| Insertion | Inferior surface of the obturator internus tendon; medial side of greater trochanter of femur with obturator internus tendon |
| Innervation | Nerve to quadratus femoris |
| Artery | Inferior gluteal artery |
| Action | Laterally rotates the extended femur at hip joint; abducts flexed femur at hip joint |
Quadratus femoris muscle
| Origin | Lateral border of ischial tuberosity |
| Insertion | Quadrate tubercle on the intertrochanteric crest of femur |
| Innervation | Nerve to quadratus femoris |
| Artery | Medial circumflex femoral artery; inferior gluteal artery |
| Action | Laterally rotates femur at hip joint |
Nerves
- Branches of Lumbar and Sacral Plexuses
- Obturator nerve (L2-L4)
- Anterior branch: innervates adductor longus and brevis, gracilis, and pectineus muscles
- Posterior branch: innervates obturator externus muscle, adductor magnus (adductor part)
- Femoral nerve (L2-L4)
- Nerve to piriformis (S1-S2)
- Nerve to quadratus femoris (L4-S1)
- Nerve to obturator internus (L5-S2)
- Superior gluteal nerve (L4-S1)
- Innervates gluteus medius, gluteus minimus, and ensor fascia latae
- Inferior gluteal nerve (L5-S2)
- Innervates gluteus maximus muscle
- Posterior femoral cutaneous nerve (S1-S3)
- Sciatic nerve (L4-S3)
- Obturator nerve (L2-L4)
Arteries
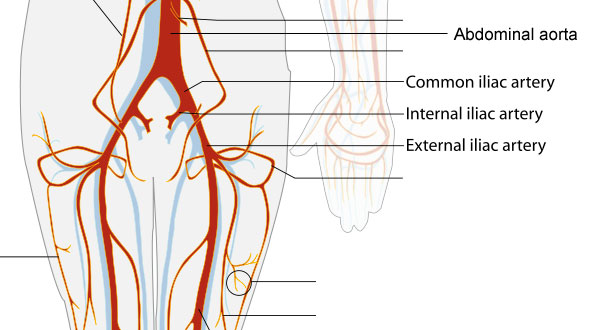
- Abdominal aorta branches into common iliac arteries
- Each common iliac artery branches into an internal iliac artery and external iliac artery
- External iliac artery
- Becomes femoral artery, which supplies the thigh
- Internal iliac artery
- Gives rise to superior gluteal artery and inferior gluteal artery, which travel with the superior and inferior gluteal nerves through the greater sciatic foramen
- Superior gluteal artery
- Travels with superior gluteal nerve
- Passes ABOVE the piriformis muscle
- Supplies obturator internus muscle, piriformis muscle, gluteal muscles, and tensor fascia latae muscle
- Inferior gluteal artery
- Travels with inferior gluteal nerve
- Passes BELOW the piriformis muscle
- Supplies muscles in gluteal region and hip joint
- Superior gluteal artery
- Gives rise to superior gluteal artery and inferior gluteal artery, which travel with the superior and inferior gluteal nerves through the greater sciatic foramen
