Learn
Upper: Shoulder, Pectoral Region, and Axilla, Arm, Forearm, HandLower: Gluteal Region, Thigh, Leg, Foot
Learn: Shoulder, Pectoral Region, and Axilla
Directions: Click on a card below to show the details for each muscle.
Note: Show tooltips by moving your mouse over text with a dotted line below.
PECTORAL REGION
This card has been intentionally left blank.
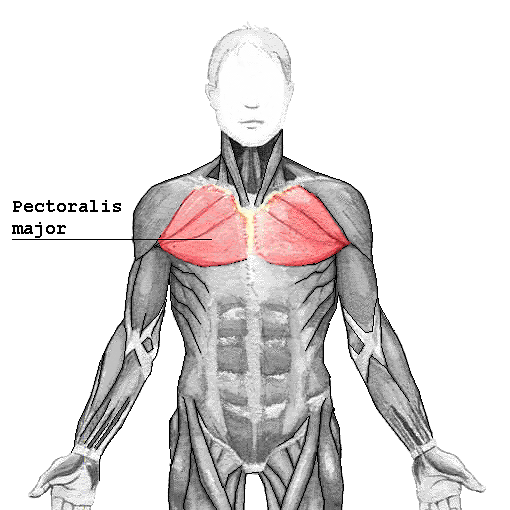
Pectoralis major muscle
| Origin | Clavicular head: anterior surface of medial half of clavicle Sternocostal head: anterior surface of sternum, superior six costal cartilages, aponeurosis of external oblique muscle |
| Insertion | Lateral lip of intertubercular groove of humerus |
| Innervation | Medial and lateral pectoral nerves |
| Artery | Pectoral branch of thoracoacromial artery |
| Action | Adduction of humerus; medial rotation of humerus; draws scapula anteriorly and inferiorly; flexes humerus (clavicular head); extends humerus from flexed position (sternocostal head) |
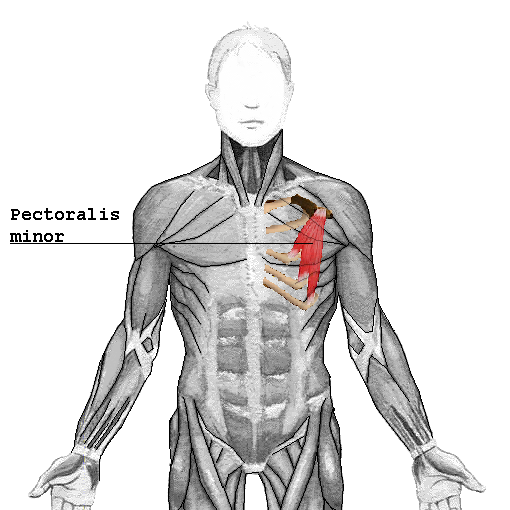
Pectoralis minor muscle
| Origin | Anterior surfaces and superior borders of ribs 3-5; deep fascia that lies over related intercostal spaces |
| Insertion | Coracoid process of scapula |
| Innervation | Medial pectoral nerve |
| Artery | Pectoral branch of thoracoacromial artery |
| Action | Draws scapula inferiorly and anteriorly to stabilize it |
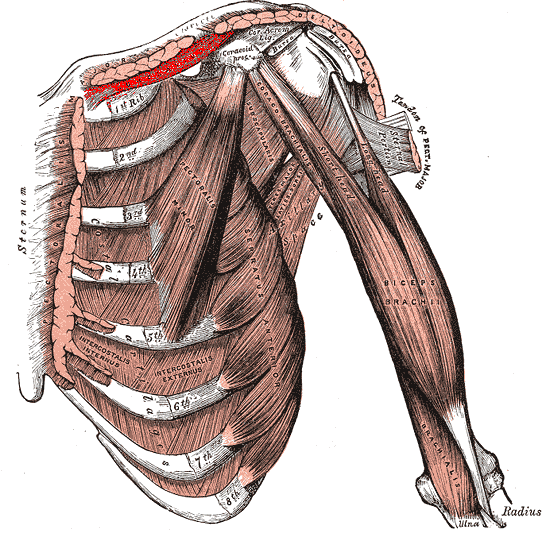
Subclavius muscle
| Origin | Junction of first rib and its costal cartilage |
| Insertion | Inferior surface of middle third of clavicle |
| Innervation | Nerve to subclavius |
| Artery | Clavicular branch of thoracoacromial artery |
| Action | Anchors and depresses clavicle |
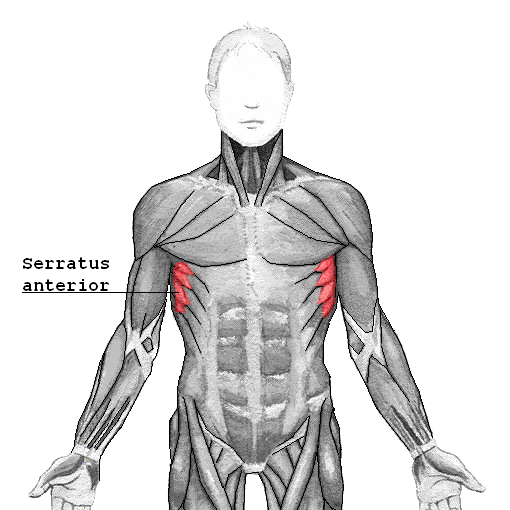
Serratus anterior muscle
| Origin | Lateral surfaces of ribs 1-8 and deep fascia overlying the related intercostal spaces |
| Insertion | Costal surface of medial border of scapula |
| Innervation | Long thoracic nerve |
| Artery | Lateral thoracic artery |
| Action | Protraction and rotation of scapula; keeps medial border and inferior angle of scapula opposed to thoracic wall |
EXTRINSIC SHOULDER MUSCLES
This card has been intentionally left blank.
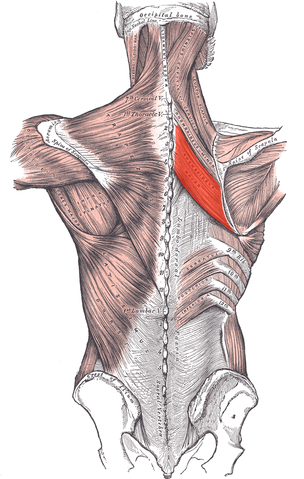
Trapezius muscle
| Origin | Superior nuchal line, external occipital protuberance, ligamentum nuchae, spinous processes of CVII to TXII |
| Insertion | Lateral one-third of clavicle, acromion, spine of scapula |
| Innervation | Motor-accessory nerve [XI]; proprioception-C3 and C4 |
| Artery | Transverse cervical artery, dorsal scapular artery |
| Action | Assists in rotating the scapula during abduction of humerus above horizontal; upper fibers elevate, middle fibers adduct, and lower fibers depress scapula |
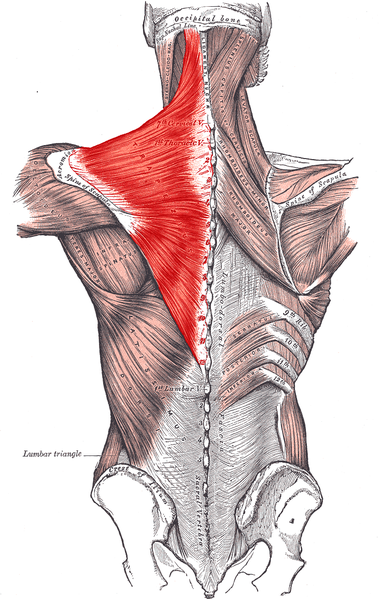
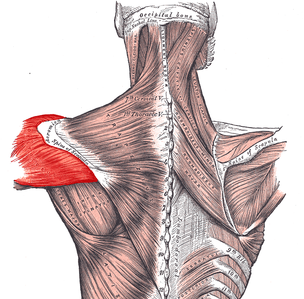
Latissimus dorsi muscle
| Origin | Spinous processes of T7-T12 and related interspinous ligaments; thoracolumbar fascia; and iliac crest; ribs 9-12 |
| Insertion | Floor of intertubercular groove of humerus |
| Innervation | Thoracodorsal nerve |
| Artery | Thoracodorsal artery |
| Action | Adducts, extends, and medially rotates humerus; raises body toward arms during climbing |
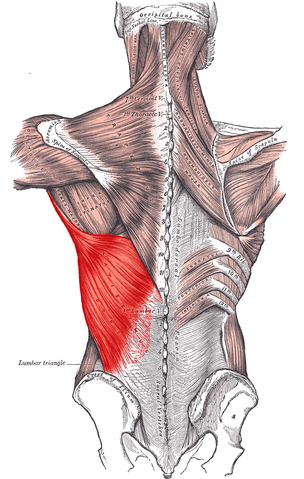
Levator scapulae muscle
| Origin | Transverse processes of CI to CIV |
| Insertion | Upper portion medial border of scapula |
| Innervation | C3 to C4 and dorsal scapular nerve |
| Artery | Dorsal scapular artery |
| Action | Elevates scapula |
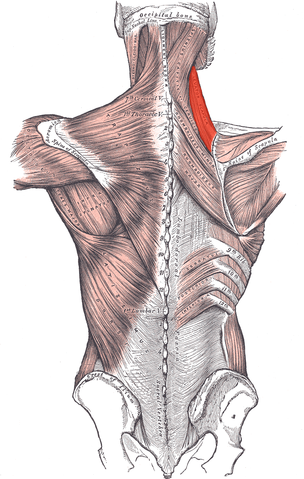
Rhomboid minor muscle
| Origin | Lower portion of ligamentum nuchae, spinous processes of CVII and TI |
| Insertion | Medial border of scapula at the spine of scapula |
| Innervation | Dorsal scapular nerve |
| Artery | Dorsal scapular artery |
| Action | Retracts (adducts) and elevates scapula |
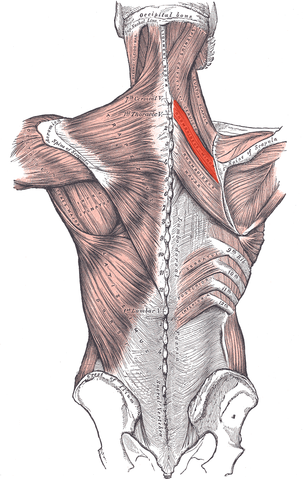
Rhomboid major muscle
| Origin | Spinous processes of TII to TV |
| Insertion | Medial border of scapula between spine and inferior angle |
| Innervation | Dorsal scapular nerve |
| Artery | Dorsal scapular artery |
| Action | Retracts (adducts) and elevates scapula |
INTRINSIC SHOULDER MUSCLES
This card has been intentionally left blank.
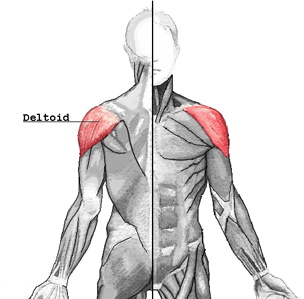
Deltoid muscle
| Origin | Lateral third of clavicle, acromion, and spine of scapula |
| Insertion | Deltoid tuberosity of humerus |
| Innervation | Axillary nerve |
| Artery | Deltoid branch of thoracoacromial artery, posterior humeral circumflex artery |
| Action | Abducts, adducts, flexes, extends, and rotates arm medially and laterally |
 |
 |
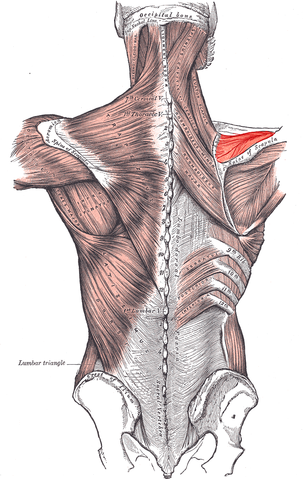
Supraspinatus muscle
| Origin | Supraspinous fossa of the scapula |
| Insertion | Most superior facet on the greater tubercle of the humerus |
| Innervation | Suprascapular nerve |
| Artery | Suprascapular artery |
| Action | Rotator cuff muscle; initiation of abduction of arm to 15° at glenohumeral joint |
Infraspinatus muscle
| Origin | Infraspinous fossa of the scapula |
| Insertion | Middle facet on posterior surface of the greater tubercle of the humerus |
| Innervation | Suprascapular nerve |
| Artery | Suprascapular artery, circumflex scapular artery |
| Action | Rotator cuff muscle; lateral rotation of arm at the glenohumeral joint |
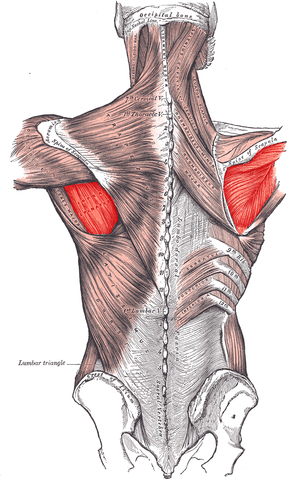
Teres minor muscle
| Origin | Middle part of lateral border of scapula |
| Insertion | Inferior facet on the posterior surface of the greater tubercle of the humerus |
| Innervation | Axillary nerve |
| Artery | Circumflex scapular artery, subscapular artery |
| Action | Rotator cuff muscle; lateral rotation of arm at the glenohumeral joint |

Teres major muscle
| Origin | Posterior surface of inferior angle of scapula |
| Insertion | Medial lip of the intertubercular sulcus on the anterior surface of the humerus |
| Innervation | Lower subscapular nerve |
| Artery | Circumflex scapular artery, subscapular artery |
| Action | Adduction and medial rotation of arm |
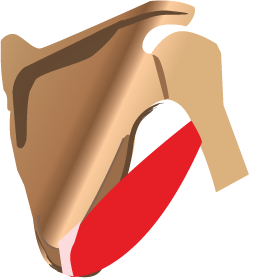
Subscapularis muscle
| Origin | Medial two-thirds of subscapular fossa |
| Insertion | Lesser tubercle of humerus |
| Innervation | Upper and lower subscapular nerves |
| Artery | Subscapular artery |
| Action | Rotator cuff muscle; medial rotation of the arm at the glenohumeral joint |
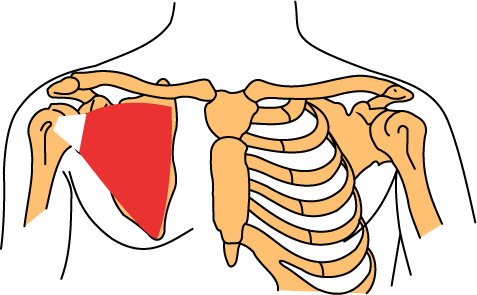
Overview
- (Right side of body) Heart → aorta → brachiocephalic trunk → right subclavian artery
- (Left side of body) Heart → aorta →left subclavian artery
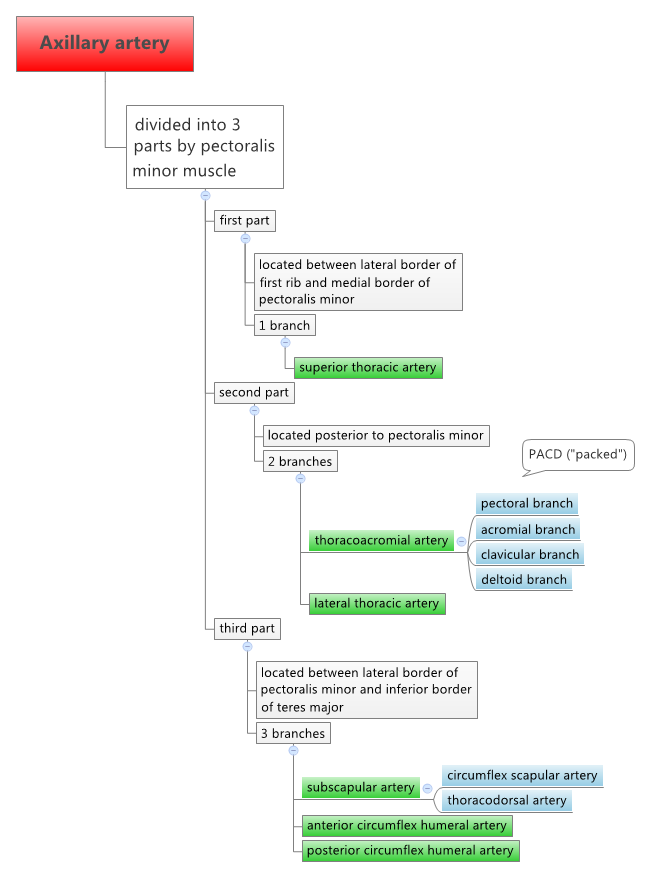
- Subclavian artery becomes the axillary artery after it crosses the first rib
- Axillary artery is divided into three parts.
- Each part has the same number of branches (i.e., part 1 has 1 branch, part 2 has 2 branches, part 3 has 3 branches) (see chart below)
- Note: Besides coming directly off of the subclavian artery, the dorsal scapular artery can also come off of the transverse cervical artery. When this happens, it is called the deep branch of transverse cervical artery.
- Each part has the same number of branches (i.e., part 1 has 1 branch, part 2 has 2 branches, part 3 has 3 branches) (see chart below)
- Axillary artery becomes brachial artery after the inferior border of teres major muscle
Subclavian Artery, Axillary Artery, and Branches
Axillary Artery
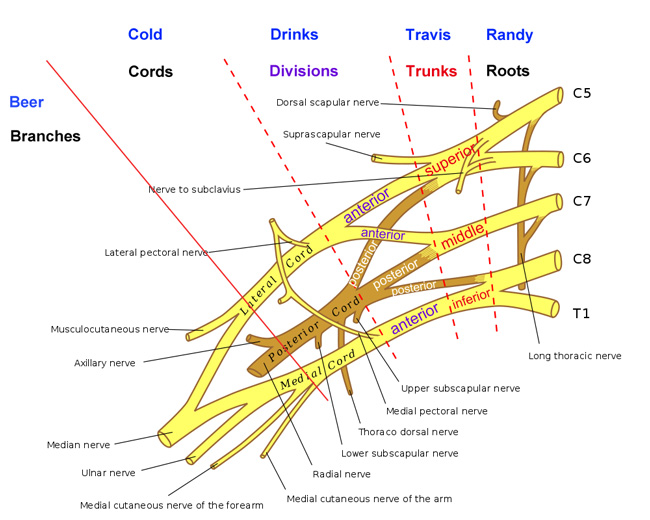
Nerves
Important Spaces in Posterior Scapular Region
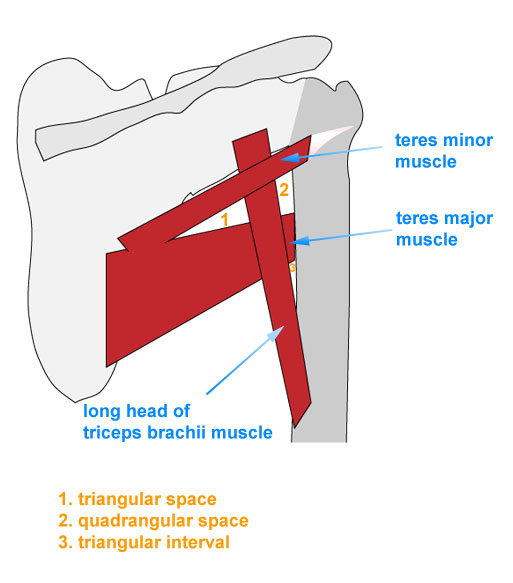
- Triangular space
- Borders
- Teres major
- Triceps brachii (long head)
- Teres minor
- Contents
- Circumflex scapular artery
- Borders
- Quadrangular space
- Borders
- Teres major
- Humerus
- Teres minor
- Triceps brachii (long head)
- Contents
- Axillary nerve
- Posterior humeral circumflex artery
- Borders
- Triangular interval
- Borders
- Teres major
- Triceps brachii (long head)
- Humerus
- Contents
- Profunda brachii artery
- Radial nerve
- Borders
Matching: Innervations of Muscles in Shoulder, Pectoral Region, and Axilla
Innervations of Muscles in Shoulder, Pectoral Region, and Axilla
Directions: Match each item correctly.
